Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) and Finite Element Analysis (FEA)
CFD and FEA are 2 types of computer-based simulation tools that can support hardtech entrepreneurs as they work through the iterative product development process.
Using CFD and FEA can help product designers evaluate initial product performance, identify potential failure points, and discover elements of the product design that could be improved. As we continue discussing the role simulations play during the product development cycle, let’s first answer a couple of important questions.
What is FEA?
FEA is a class of software that allows hardtech entrepreneurs to conduct structural analyses of a solid product. FEA software predicts how a physical product might behave when the forces and pressures of real life are applied to it.
“Analyzing structural integrity when factors like vibration, friction, and heat or cold are applied can help the product developer make informed decisions,” explains Bill Fienup, mHUB Co-Founder and Director of Innovation Services. “Static and dynamic simulations can be done on singular products or product assemblies, and this can provide information to the product developer about if/where/how the product might physically break – or if there may be a design flaw that creates a weak point to be addressed.”
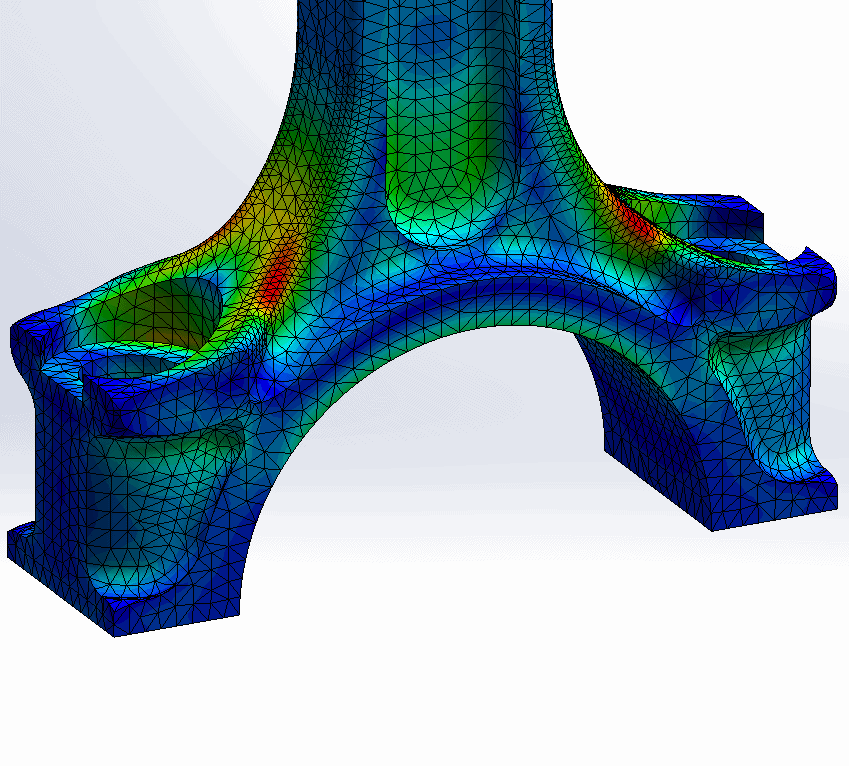
(Image of Finite Element Analysis (FEA) Courtesy of Fastway Engineering).
Pamela Silva, Founder of PamLab Design and Engineering and new member of the Hardtech Development fellowship program adds, “finite element analysis can be useful to identify the locations within a part that will be subjected to high stresses and can potentially lead to part failure. With this information, you can think of and model changes in your geometry to extend the life of your product.”
In addition to analyzing the structural integrity of a product in development, computational fluid dynamics can be combined with FEA to understand the behavior of a fluid as it exists within or moves through a physical product.
What is CFD?
CFD software platforms simulate the behavior of fluids. “CFD analysis is more complex than that of FEA,” states James Shaw, Managing Director of Fastway Engineering and engineering consultant who works with mHUB Hardtech Development services. “A solid is a solid, but a fluid can be many things. Its density and viscosity can vary, the flow can be laminar or turbulent, and the fluid can even transition between various states, such as boiling, condensation, cavitation, etc.”
CFD is a fluid analysis that simulates how different types of liquid materials flow through and around objects, providing insight on how the liquids behave and affect the physical structures with which they are interacting.
“CFD is something you would want to use when you are considering smart products for water management or cooling for high-density powered electronics; it can help you understand issues around heat transfer and thermal management,” continues Shaw.
“Computational fluid dynamics can also be used to model the behavior of an object submerged in a fluid, such as water or air. It can provide insights for developments in wind and hydrokinetic energy technology, among other applications,” expounds Silva.
The role CFD & FEA simulations play during the product development cycle
Hardtech innovators typically utilize CFD & FEA during the conceptual design of a new product or the optimization of an existing product. “When you break it down, product development is simply a series of making decisions,” says Shaw. “If you get to a point where you must make a design decision, and you’re missing so much information that you’re uncomfortable making that decision, this is where simulation can be leveraged to help you understand what you don’t know.” Running simulations can help reduce the time it takes to develop the product, and in many cases, reduce the costs to develop a new product.
There is one misconception about CFD & FEA simulation that needs to be addressed. Some people may think that simulation replaces testing, but the reality is that simulation and testing go hand-in-hand.
“It’s expensive to test. It’s the recurring time to make prototype after prototype and re-test, so simulations can be introduced to reduce the iterations on the testing,” shares Shaw. “Because the product design is digital, there is practically no lead time on regenerating a CAD file. Best practice is to have a testing program AND a simulation program at the same time. You should run them in tandem while you are measuring and tuning your analyses. If the simulations match the test results, you can start to build confidence in the model and reduce the resources allocated to testing.”
Hardtech startups often do not have the historical test data to rely on as they are disrupting the market with fresh, innovative ideas. With no test data readily available, mechanical engineering simulation can help fill in the gaps.
“People may not realize the resources that are available when it comes to using simulation software,” states Fienup. “With tools like ANSYS, Autodesk, PTC CREO, and SolidWorks, plus strategic help from the mHUB Community, software simulation can be introduced to any physical product development project.”
If you are unsure how to integrate simulation into your product development cycle, complete the form below to reach out to the team at mHUB Hardtech Development services.





